CSS- BOX CONCEPT Simple Introduction
👉Cascading Style Sheets
INTRODUCTION :
Cascading Style Sheets(CSS),It is the language for describing the presentation of web
pages, including Colors, layout and fonts, thus making our web pages presentable to the users.CSS is
designed to make style sheets for the web.
👉Syntax For CSS:https://youtu.be/q_4kIgC4C30?si=86_expgR3nDoAy8G
Introduction to CSS Box Model:
Cascading Style Sheet provides the styling HTML elements. But, for styling an element, we must know about HTML elements and their behavior as far as CSS is considered. One of the most important parts of designing a web page is deciding the layout. If the placements of elements on the page are properly planned, it can be made dynamic and responsive. The presentation of the page depends upon how the elements have been rendered. In plain HTML, if we use different elements, they are rendered one after the other in a queue form. However, CSS allows us to customize that part of the display, which this article will discuss in detail. This property of CSS is called the Box Model. Each element can be equated to a box, and CSS lets the developer decide various parameters of this box to customize each element’s rendering and create the page’s overall layout.
link here: https://youtu.be/4J2Cfni-ANM?si=MccdGdWXSN1magSv
Box Model Elements :
There are four elements in a box model on which the behavior of the box (element) relies. These are:
- Content: This is the main content of the element. It can be text, links, images, videos, or other content.
- In HTML, everything behaves like a box. Let's insert some content with a kitty image. 👇
- Padding: This is the gap between the content and the content’s border (another element).
2nd box-model layer: Padding
The next layer of the CSS box model is the padding layer. It wraps our content like this 👇
- Border: This can be visualized as a solid boundary of the element’s content.
3rd box-model layer: Border
The next layer of the CSS box model is the border layer. It wraps our content + padding like this 👇
4th box-model layer: Margin
The next and final layer of the CSS box model is the margin layer. It wraps our content + padding + border like this 👇
Table of Contents
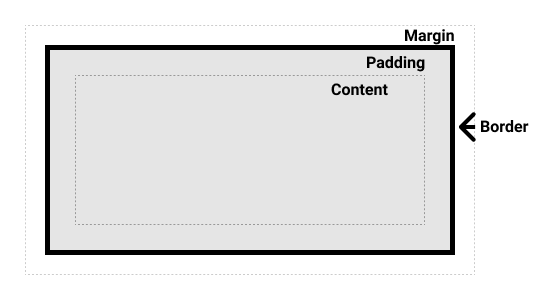
The standard CSS box model:
- In the standard box model, if you give a box an
inline-sizeand ablock-size(orwidthand aheight) attributes, this defines the inline-size and block-size (width and height in horizontal languages) of the content box. - Any padding and border is then added to those dimensions to get the total size taken up by the box
The alternative CSS box model:
- In the alternative box model, any width is the width of the visible box on the page.
- The content area width is that width minus the width for the padding and border (see image below).










Comments
Post a Comment